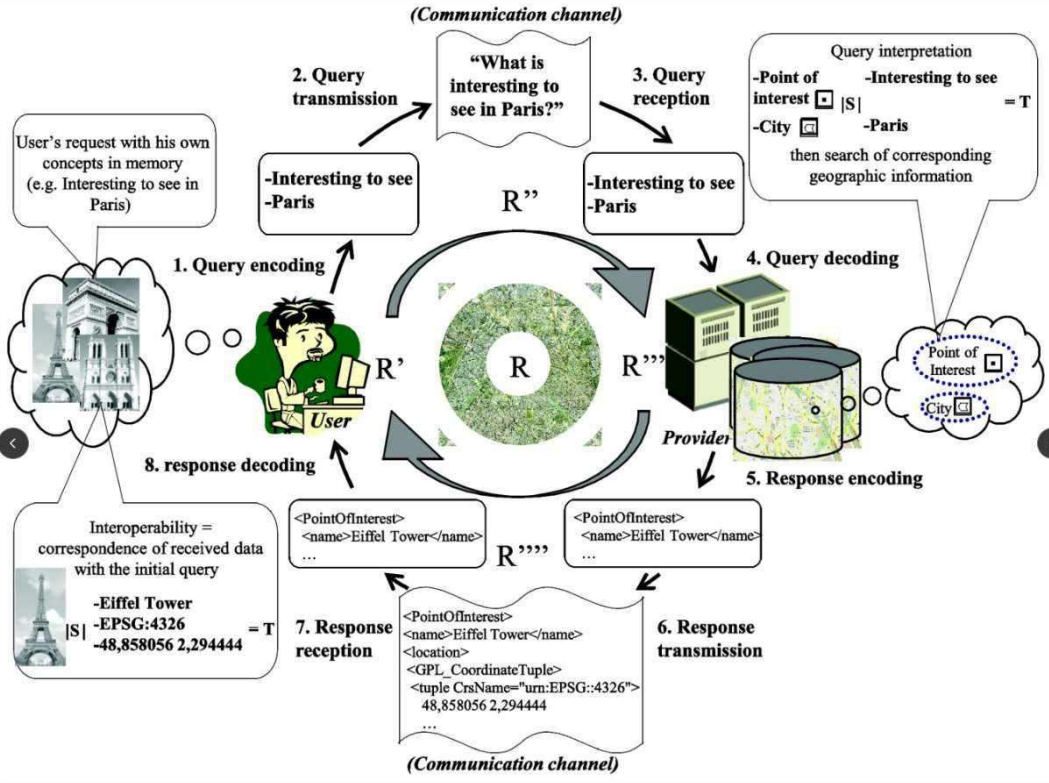
GIS
SES.pdf
Spatially Enabled Society (SES)
- is one that makes use and benefits from a wide array of spatial data, information, and services as a means to organize its activities
- the concept where location, place and other spatial information and services are ubiquitously available to governments, citizens and businesses as a means of organising their activities
- such data and information must be available in a free, efficient, and comprehensive way
- it therefore needs to be organized in such a way that it can easily be shared, integrated, and analysed
Spatial enablement (1)
- the ability to add location to almost all existing
information
- uses the concept of place and location to organize
information and processes
- requires (spatial) information to be collected, updated,
analysed, represented, and communicated
- depends primarily on the spatial data infrastructure (SDI)
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Data input & Data processing → Database management → Data output
Spatial enablement
- Global Positioning System (GPS): on 1 May 2000,
Selective Availability (a means of reducing the precision of civilian receivers) was definitively switched off, improving navigation accuracy to at least 20 m instead of the previous 100 m
- developments in mobile telephony
- smartphones (from 2007)
- broadband cellular networks (3G, 4G, 5G, …)
- Geo-tagged Photographs or Video material
- Geo-located tweets
- GPX Trails
- POI Provision
- Geo-social networking
- Edit/Update Contributions
1962 - CGIS Roger Tomlinson Father of GIS
1969 - Internet
1990 - WWW Tim Berners-Lee Father of the Web (URL, HTTP, HTML)
1993 - Web GIS Xerox PARC Viewer
Global Reach: large number of users, better cross-platform, low cost, easy to use, diverse applications
AJAX
- Asynchronous
- Javascript
- XML
GIS vs Consumer Mapping
- GIS user communities
- State, Local and Federal Government
- Utilities industries
- Surveying and mapping
Consumer mapping user communitiesSpatially enabled citizensConsumers
Retail business
- Real estate (needs GIS too)
Consumer mapping usesStore locator
Driving directions
Points of interest
- GIS uses
- Planning and analysis
- Buffering
- Feature and drill down queries
Key concepts in Consumer Mapping
Tiles, notvector data
Map themes, notlayers(road, aerial, hybrid)
- Integrated search
Web Mercator, Google Web Mercator,
Spherical Mercator, WGS 84 Web
Mercator, WGS 84/Pseudo-Mercator
- Searching
- Finding directions (shortest route)
Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI)
- the infrastructure that facilitates the discovery, access,
management, distribution, reuse, and preservation of
digital geospatial resources
- these resources may include maps, data, geospatial
services, and tools
- as cyberinfrastructures, SDIs are similar to other
infrastructures, such as water supplies and
transportation networks, since they play fundamental
roles in many aspects of the society
Data & Service Providers = Data + Services
Geoportal = Metadata DBMS + Web interface
GIS Users = Tablets + Laptops + Phones
Data & Service Providers — publish —> Geoportal
Geoportal ← Search & discover → GIS Users
GIS Users — Consume → Data & Service Providers
Geoportal:
- a gateway website through which people can search,
discover, access, and visualize the geospatial
resources within a SDI (spatial data infrastructure)
- these resources may include maps, data, geospatial
services, and tools
Thematic_maps_QGIS.pdf
- Single symbol
- Simple fill
- Select color:
- Color ramp
- Color wheel
- Color swatches
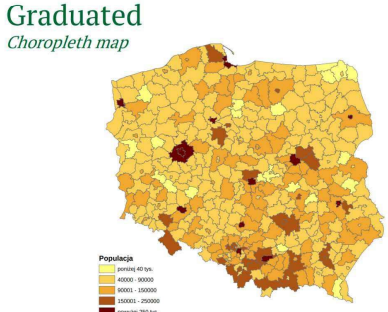
- Categorized
- Graduated (choropleth map)
- Histogram
Classification modes
- Equal Count (Quantiles)
- Each class contains the same number of features
- Quantile classification is good when studying data with a linear distribution
- Similar features can end up in different classes, or completely different in one class — such distortion can be reduced by increasing the number of classes
- Equal Interval
- This classification method divides a set of attribute values into a specified number of classes with an equal range of attribute values
- This is an excellent way to present similar data percentage type, as well as temperature
- Fixed Interval
- A method similar to the equal interval method, the difference being that in this method users define the size of the interval themselves
- Natural Breaks (Jenks) / Natural intervals
- Classes are based on naturally grouped values - the program identifies breaks by looking for groups and patterns in the data.
- Features are subdivided into classes whose boundaries have created at locations of large jumps in the value of the data.
- Standard Deviation
- This method of classification shows the deviation of attribute values from the mean
- Two-colour scale helps to represent values above and below average
<<< Przykłady map >>>
Graduated - Size
Provider feature filter
Dot (density map)
Random Points inside polygons
Diagrams - Histogram
Diagrams - Pie Chart
Multiple attributes
Labels
Single Labels
Expression builder
Example expression:
'Ludnosc miejska: ' || round("Ludnosc_mi" / 1000, 0) || ' tys.' || '\n' ||
'Ludnosc wiejska: ' || round("Ludnosc_ws" / 1000, 0) || ' tys.'Example functions:
round ("“FIELD", n) \n)
lower ("FIELD") e.g. OPOLSKIE — opolskie
upper ("FIELD") e.g. Opolskie — OPOLSKIE
Data defined override
Rule-based labeling
Edit rule
Thematic_maps_GUS.pdf
Thematic map
- portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area
- use map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features (phenomena) that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population
- they contrast with general reference (base, topographic) maps, which focus on the location (more than the properties) of a diverse set of physical features, such as rivers, roads, and buildings
Statistics Poland
- formerly known in English as the Central Statistical Office
- in Polish: Główny Urząd Statystyczny (GUS)
- Poland's chief government executive agency charged with collecting and publishing Statistics related to the country's economy, population, and society, at the national and local levels
- Local Data Bank
- GUS Geostatistics portal (GUS Portal Geostatystyczny)
- Statistics Poland
Geostatistics (Wikipedia)
- a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets
- Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations.
- Is intimately related to interpolation methods but extends far beyond simple interpolation problems.
- Geostatistical techniques rely on statistical models that are based on random function (or random variable) theory to model the uncertainty associated with spatial estimation and simulation.
- Not to be confused with statistical geography.
- The study and practice of collecting, analysing, and presenting data with a geographic or areal dimension, such as census or demographic data.
- It uses techniques from spatial analysis but also encompasses geographical activities such as the defining and naming of geographical regions for statistical purposes
Map portal - GUS data
- Add statistical Layer
- Export layers
- Print editor → print to pdf
Q-GIS_intro.pdf
GPS - Global Positioning System (GNSS - Global Navigation Satellite System)
Trilateral → involving three groups or countries:
- Trilateration From Satelites is the Basis of the System
- To Trilaterate, GPS Measures Distance Using the Travel Time of a Radio Signal
- To Measure Travel time, GPS needs very accurate clocks
- In addition to knowing the distance to a satellite, a User needs to know the Satellite’s location
- As the GPS signal travels through the lonosphere and Earth’s atmosphere it gets delayed
Sextant - kątomierz lusterkowy
Plane table survery
Definition
A system for acquiring, processing and sharing data that contains spatial information and accompanying descriptive information about objects identified in the part of space
covered by the system. - Systemy informacji przestrzennej
Spatial/geographic(al) information
“Information about the location, geometric properties and spatial relationships of objects that can be identified in relation to the Earth. The concept of object here is broad, encompassing not only permanent natural and artificial objects, but also natural, social and economic phenomena.” [Systemy informacji przestrzennej J. Gaździcki]
Geographic Information System (GIS)
- is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all types of data.
- GIS connects data to a map, integrating location data (where things are) with all types of descriptive information (what things are like there) [esri.com].
- This provides a foundation for mapping and analysis that is used in science and almost
every industry.
- GIS helps users understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context.
- The benefits include improved communication and efficiency as well as better management and decision making [esri.com].
Data models
- vector (points, linestrings. polygons)
- customers
- streets
- raster (grid)
- elevation
- land usage
- TIN - Triangular Irregular Network
- (tabular)
Thematic layers (przykład Rezerwat przyrody)
- Rejony administracyjne
- Lasy liściaste
- Rzeki
- Stanowiska roślin chronionych
- Ścieżki
- Tablice informacyjne
- Ortofotomapa terenu
- Data processing
- Data output
GIS applications
- Thematic maps
- 3D visualization
- Cadastral maps (mapy z działkami i domami)
- Spatial analysis
Example: QGIS (formerly Quantum GIS)
Three basic components:
- QGIS Desktop
- QGIS Browser
- Processing Toolbox
Vector data formats
- Shapefiles
- Spatial databases
- GeoPackage
- SpatiaLite
- PostGIS
Raster formats (GDAL)
TIFF/GeoTIFF (*.tif + .tfw)
ArcInfo ASCII Grid (.asc)
ERDAS IMAGINE (*.img)
Esri GRID (without extension — folder)
BMP (*.bmp + .bpw), GIF (.gif + .gfw), PNG (.png + .pgw)
GRIB — used in meteorology (.grb)
Surfer (*.grd)
Intergraph (*.cit, *.cot)
MrSID (*.sid + *.sdw)
JPEG (*.jpg + *.jgw), JPEG 2000 (*.jp2, *.j2c, *.j2k, *.jpx)World file
ArcInfo ASCII Grid
Bith depths (number of bits per pixel)
Compression methods (lossy and lossless)
Lossy: JPEG, JPEG 2000 - reszta Lossless
Geoid → ellipsoid
Ellipsoid globally best fitting to the geoid
- Coordinate Reference Systems (CRS)
- none (or WGS84)
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
Map projection families
Cartographic (map) projections
Coordinate Reference Systems (CRS)
- Robinson (balanced)
- Mercator (conformal)
- Azimuthal (equidistant)
- Mollweide (equal area)
- Bonne
- Fuller
- Goode Homolosine (Ocean)
- EPSG
- WGS84
- Pulkovo 1942(58)/Poland zone I
- PL-2000 zone 7
- PL-1992
epsg.io
Coordinate Systems Worldwide
Tablular data:
- attribute tables
- dBase files (*.dbf)
- tables in databases
Data types in tables
- Integer (32 bits)
- Integer (64 bits)
- Decimal number (real)
- Text (string)
- Date
Length and precision
- Length — the number of digits in the number together before and after the decimal point, or (for texts and integers) the column width
- Precision — number of digits after decimal point